Managed Service Providers (MSPs) serving small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) must elevate their game in 2026 to meet rising expectations and rapid technology changes. Globally, the MSP market continues to expand (projected at $424–$511 billion by 2026), and SMBs are channeling unprecedented investments (over $90 billion in new managed IT spending through 2026). However, with this opportunity comes intense pressure: clients demand better cybersecurity, optimized cloud services, meaningful use of AI, improved service experiences, strict compliance, greater automation, and skilled support. Many MSPs today struggle with gaps in these areas – from reactive security postures to talent shortages – which must be addressed for sustained growth. [deskday.com]
The table below summarizes key operational areas, where MSPs often fall short at present, and the essential focus and actions needed in 2026 to improve:
| Area | Current Gaps / Needs Improvement | 2026 Focus & Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity | Reactive approach prevalent; advanced threat detection, incident response, and user security training are often insufficient [provaltech.com]. | Adopt 24/7 threat monitoring (MDR/SOC), implement zero-trust & MFA, run regular security awareness training, and offer compliance guidance (e.g. PCI/GDPR) [deskday.com], [provaltech.com]. |
| Cloud Services | Focus often limited to migration; many lack expertise in multi-cloud management, cost optimization, and robust cloud security [deskday.com]. | Provide end-to-end cloud support: manage hybrid/multi-cloud environments, practice FinOps for cost control, ensure cloud backup & DR, and leverage edge computing for low-latency needs [deskday.com], [deskday.com]. |
| AI Integration | Slow adoption of AI – only ~30% of MSPs use AI to automate tasks, as others remain cautious or lack skills [kaseya.com] (smaller MSPs risk falling behind larger competitors [channele2e.com]). | Embed AI in operations: deploy AI-driven ticket triage/chatbots for Tier-1 support, use predictive analytics to prevent outages, and develop client-facing AI solutions (e.g. deploying productivity AI tools) [deskday.com], [channele2e.com]. |
| Customer Experience | Often seen as mere IT vendors rather than strategic partners – value reporting and proactive guidance lag behind client expectations [channele2e.com]. | Elevate client engagement: act as a vCIO with business-aligned IT roadmaps, conduct outcome-focused QBRs, provide transparent ROI dashboards (e.g. uptime improved, incidents prevented), and personalize support [channele2e.com], [provaltech.com]. |
| Compliance & Governance | Proactive compliance management is not standard – many SMBs lack guidance on regulatory requirements and data governance [deskday.com]. | Offer compliance-as-a-service: audit and ensure adherence to standards (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI), deliver automated compliance reports, and keep clients ahead of regulatory changes (adopt “compliance-first” service design) [deskday.com], [deskday.com]. |
| Process Automation | Operations still too manual – MSPs waste 100+ hours/month on tasks (ticket entry, reporting) due to disjointed tools and <25% workflow automation [suppfusion.com], [suppfusion.com]. | Maximize automation: integrate PSA/RMM and other tools to eliminate duplicate data entry [kaseya.com], use scripts/RPA for routine maintenance, auto-generate reports (e.g. for QBRs) to free time for strategic work [suppfusion.com], [suppfusion.com]. |
| Workforce Development | Skill shortages and burnout persist – over 52% of MSPs cite hiring skilled staff as a top challenge [deskday.com], and overworked teams (59% working holidays) reflect understaffing [kaseya.com]. | Bolster talent and capacity: invest in upskilling (certifications, training) [provaltech.com], improve work-life balance by offloading work (e.g. outsource NOC/SOC via white-label partners) [deskday.com], and create clear career paths to retain experts [provaltech.com]. |
Below, we dive into each of these focus areas, examining what MSPs are not doing well today and how they can improve in 2026, with examples and global trends in mind.
1. Strengthening Cybersecurity & Resilience
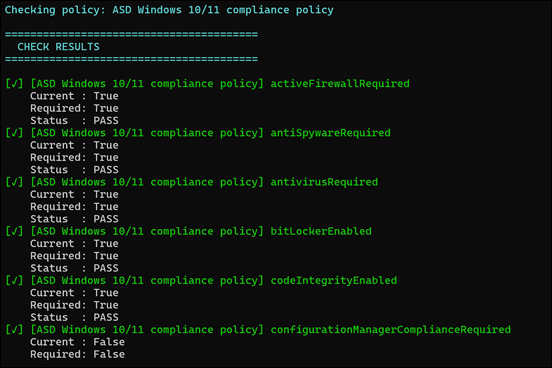
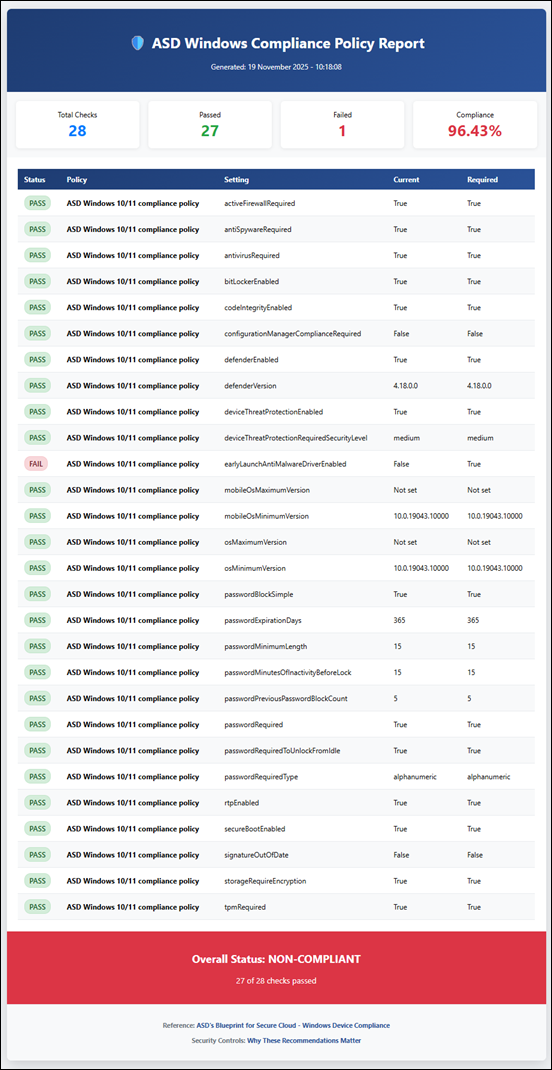
Cybersecurity is the number-one growth driver in managed services, yet many MSPs’ security offerings haven’t kept pace with evolving threats. What’s not done well: Too often, MSP security is reactive – providing basic antivirus, firewalls, and backups – but lacking in proactive threat hunting, continuous monitoring, and incident response planning. Many providers still treat security as an add-on, rather than baking it into every service. Crucially, clients now expect more: they want their MSP to be a comprehensive security partner, handling advanced threats and compliance needs, not just a help-desk for cyber issues. For example, SMBs are increasingly asking MSPs for help with compliance and cyber insurance requirements – areas in which some MSPs are underprepared. [deskday.com] [provaltech.com]
Focus for 2026: MSPs must shift from reactive to proactive security. This means adopting 24×7 threat monitoring and rapid response capabilities. For instance, a provider might set up a managed detection and response (MDR) service or partner with a Security Operations Center (SOC) to monitor client networks around the clock for intrusions. MSPs should implement zero-trust security frameworks (verify every user/device), enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA) everywhere, and regularly test backup and disaster recovery plans. Security awareness training for client employees is also key – many breaches start with human error, so MSPs should run phishing simulations and training sessions to harden the human element.
Moreover, expanding compliance services is critical. Compliance has become “table stakes” for clients in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Yet not all MSPs offer systematic compliance support today. In 2026, leading MSPs will offer Compliance-as-a-Service – e.g. continuous monitoring of compliance (using tools aligned to standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, GDPR), automated audit reporting, and guiding clients through regulatory changes. An MSP might, for example, maintain a compliance dashboard for each client that tracks data backup practices, access controls, software patch levels, and other policy requirements in real-time. By doing so, the MSP not only protects the client’s data but also helps them avoid fines or legal issues. [deskday.com]
Example Action – Cybersecurity: One MSP serving many SMB law firms realized its basic security package was insufficient. In 2026, it invested in an AI-enhanced threat detection system and partnered with a specialized managed SIEM provider to filter and analyze logs across all client sites. It also began conducting quarterly security posture reviews for each client, showing how many attacks were blocked and recommending next steps (like encrypting all mobile devices). This proactive stance not only reduced incidents but also reassured clients with compliance concerns (e.g. demonstrating support for GDPR and emerging privacy laws). As a result, the MSP could “command premium pricing” for its security-centric services while building deeper trust with customers. [deskday.com]
In summary, cybersecurity in 2026 should permeate every aspect of an MSP’s offerings. The MSPs that succeed will be those who anticipate threats (using advanced tools and intelligence), respond swiftly to incidents, and ensure clients meet security compliance mandates. Given that cybersecurity services are growing ~18% annually (faster than the overall MSP market), investing in these capabilities is both a defensive move and a major growth opportunity. [deskday.com]
2. Optimizing Cloud Services & Infrastructure
Cloud services have become a core component of SMB IT strategies worldwide, but MSPs often struggle to move beyond basic cloud enablement. Current weaknesses: Many MSPs excel at initial cloud migrations (moving an SMB’s servers or applications to AWS/Azure or a private cloud), but fall short in ongoing optimization and multi-cloud expertise. As more businesses adopt complex architectures – e.g. hybrid clouds (mix of on-prem and cloud) and multi-cloud deployments – MSPs need deeper skill in managing and optimizing these environments. In practice, some providers still treat cloud management as a set-and-forget hosting task, missing opportunities to fine-tune performance, optimize costs, or update security configurations continuously. SMB clients, however, increasingly expect their MSP to be the cloud expert who can navigate these complexities: nearly 48% of SMBs now rely on MSPs for public cloud management (a figure climbing each year). [deskday.com]
Focus for 2026: End-to-end cloud lifecycle management should be a priority. MSPs must go beyond provisioning to deliver ongoing optimization, cost management, and integration across cloud platforms. One key area is cost optimization (FinOps) – cloud costs can spiral out of control for SMBs who lack the expertise to right-size resources. An MSP in 2026 should regularly analyze clients’ cloud usage, eliminate waste (e.g. unused VMs or over-provisioned storage), and advise on reserved instances or savings plans. This proactive cost management demonstrates tangible value. In fact, experts note that MSPs should invest in cloud optimization capabilities to meet evolving demand. [channele2e.com]
MSPs also need to handle multi-cloud and hybrid environments confidently. With 73% of organizations using hybrid cloud and multi-cloud adoption doubling in recent years, a provider might, for example, manage an SMB’s Azure infrastructure alongside a Salesforce SaaS and an on-prem file server – ensuring they all work together. Skills in cloud orchestration and monitoring tools (that work across AWS/Azure/GCP) are essential. Security in the cloud is another improvement area: MSPs should implement cloud security best practices like regular cloud vulnerability scans, proper identity & access management, encryption of data at rest and in transit, and configuration audits (using benchmarks such as CIS benchmarks for cloud). [deskday.com]
Emerging technologies present both a challenge and opportunity. Edge computing and IoT integration are on the rise, especially for industries needing real-time data processing (manufacturing, retail, smart devices). In response, MSPs should be prepared to manage distributed edge infrastructure – for example, deploying and monitoring mini-servers or appliances at client sites or in the field that sync with central cloud systems. By developing solutions for edge computing (like local data processing coupled with cloud analytics), an MSP can differentiate itself for clients who require low-latency performance. [deskday.com]
Example Action – Cloud: An MSP with several SMB clients in e-commerce noticed their cloud bills were climbing while performance issues lingered. In 2026, the MSP introduced a Cloud Cost & Performance Audit service. Using cloud management tools, it analyzed each client’s resource utilization and identified overspending (e.g. servers running at 5% utilization). It then implemented auto-scaling and schedule-based resources (shutting down non-critical systems after hours) for those clients, cutting cloud costs by 20%. They also added a multi-cloud backup solution – replicating critical data from the primary AWS environment to an Azure data center – to bolster resilience. The clients not only saved money but also gained confidence that their cloud setup was optimized and fault-tolerant, something they wouldn’t have achieved on their own.
In short, MSPs in 2026 should provide holistic cloud stewardship: from architecture planning and migration through continuous optimization, security, and new tech integration. As SMBs continue to increase spending on cloud and related services, MSPs who deliver efficiency and reliability in the cloud will deepen customer loyalty and attract new business. [channele2e.com]
3. Embracing AI-Driven Solutions and Automation
AI integration is shifting from a buzzword to a competitive necessity for MSPs. By 2026, AI won’t be optional – it will be woven into service delivery for efficiency and smarter support. Where MSPs are lagging: A surprising number of MSPs have been slow to leverage AI in their operations. Surveys show roughly 30% of MSPs are already using AI to eliminate repetitive tasks, but the majority have not yet implemented such solutions, with some firms cautious about AI’s risks or lacking in-house expertise. This reluctance is problematic: AI is rapidly changing MSP economics by automating Tier-1 support tasks, and providers not leveraging AI will struggle to compete on cost and service quality. In essence, larger MSPs (often backed by investors) are racing ahead with AI, widening the efficiency gap over smaller players. [kaseya.com] [channele2e.com]
Focus for 2026: MSPs should embed AI across their workflows to enhance both internal efficiency and customer value. A primary application is in the service desk: deploying AI-driven chatbots or virtual agents that can handle common support queries and basic troubleshooting. By 2026, an AI-powered system can automatically categorize and route tickets, suggest solutions, or even resolve issues (like password resets or simple network glitches) without human intervention. In fact, analysts predict widespread service desk automation could cut ticket volumes by 40–60% and drastically speed up resolution times. This frees up human technicians to focus on more complex issues, improving overall support quality. It’s telling that 87% of MSPs plan to increase AI investments by 2026 – the tools are becoming more accessible (built into RMM/PSA software, for instance) and MSPs recognize the ROI. [deskday.com]
Beyond support, predictive analytics is a game-changer. MSPs should use AI to analyze system logs and performance metrics to predict and prevent failures – for example, forecasting when a server might fail or when storage will run out, so they can fix it before it causes downtime. This predictive maintenance approach was once a luxury but is increasingly expected as part of proactive managed services.
MSPs can also extend AI to augment decision-making and reporting. Modern AI tools can comb through an SMB client’s data and provide insights, such as identifying security anomalies or highlighting usage trends. Some MSPs are starting to use generative AI to draft clearer client communications or create executive summaries of IT performance for quarterly reports. In 2026, we’ll see successful MSPs providing clients with AI-generated insights – for example, an automated monthly report that not only lists incidents resolved, but explains in plain language how those IT events affected the client’s business and recommends improvements (all generated with minimal human editing). [deskday.com]
Furthermore, MSPs should consider offering AI-related services to customers. SMBs often lack the knowledge to implement AI solutions themselves, so an MSP can step in as a guide. This could include setting up an AI-powered analytics platform for a client’s sales data, or integrating an AI chatbot on a client’s website for customer service. Since 55% of businesses expect their MSPs to adopt and deploy AI tech by 2026, showing expertise in practical AI applications can be a major selling point. [deskday.com]
Example Action – AI: A mid-sized MSP in 2025 handled thousands of tickets monthly and struggled with slow response times. In 2026, they integrated an AI service bot into their ticketing system. The bot uses natural language processing to understand incoming emails and chat requests from users – it automatically resolved simple issues (password resets, Wi-Fi setup instructions) and pulled up relevant knowledge base articles for technicians on more complex problems. The result was a 50% reduction in human-handled Level-1 tickets and much faster first responses. Additionally, the MSP began offering an “AI Advisory” service to clients: helping SMBs pilot tools like Microsoft’s AI Copilots or AI-based CRM add-ons to streamline their own business workflows. This not only generated a new revenue stream but also positioned the MSP as an innovation partner.
In sum, AI and automation are key to MSP efficiency and differentiation in 2026. MSPs should aim to automate away the grunt work – from repetitive troubleshooting to data reporting – so they can deliver faster service at scale. Those who fail to leverage AI will find themselves with higher costs and slower service, unable to match “AI-powered” competitors. Embracing AI is thus both a defensive strategy (to stay efficient) and an offensive one (to offer new intelligent services). [channele2e.com]
4. Enhancing Customer Experience and Strategic Value
As technology solutions commoditize, customer experience (CX) and the strategic value an MSP provides become critical differentiators. Today’s SMB clients don’t just want IT support; they want a partner who understands their business and helps it grow. Where MSPs fall short: Many MSPs still operate in a reactive, technical mindset – fixing what’s broken and maintaining systems – but not engaging at the business level or clearly demonstrating value. Clients are increasingly scrutinizing costs and asking, “What am I getting for this monthly fee?”. If the MSP only talks in technical terms (uptime, tickets closed) without linking to business outcomes, clients may feel the partnership is not delivering enough. In fact, MSP industry experts observe that successful MSPs now “sell outcomes, not just services,” using benchmarks and reviews to prove their worth. Many providers have been slow to adopt this outcomes-focused approach. [channele2e.com]
Another aspect of CX is responsiveness and personalization. SMB customers can feel neglected if their provider treats them like just another ticket number. Some MSPs could do better in maintaining regular communication, soliciting feedback, and tailoring their support to each client’s unique needs. It’s telling that clients are asking for more guidance – for example, they want help choosing which software matters, which investments to prioritize, and clarity on why MSP recommendations are made. If MSPs aren’t providing this guidance, clients may seek someone who will. [provaltech.com]
Focus for 2026: MSPs should strive to become trusted advisors to their SMB clients, not just IT fixers. This means deeply understanding each client’s industry, business goals, and challenges, and then aligning technology strategies accordingly. A concrete step is to institute regular strategic meetings – often Quarterly Business Reviews (QBRs) – but these must evolve from perfunctory report-outs to forward-looking planning sessions. Rather than just reciting metrics, the MSP should use QBRs to discuss “Here’s how your IT environment improved your business this quarter, and here’s what we recommend for the next quarter to support your goals.” For example, tie in how a new collaboration tool led to faster project completion for the client, or how the MSP’s quick incident response saved X hours of downtime, preserving the client’s revenue. Actionable outcomes should be the focus of these meetings. [provaltech.com]
To support these strategic discussions, MSPs need to provide clear, tangible reporting of value. Gone are the days of sending a generic monthly uptime report that clients might not even read. In 2026, MSPs should leverage dashboards and analytics to show key performance indicators (KPIs) that matter to the client’s leadership – whether it’s the number of cyber attacks blocked (indicating risk reduction), the time to resolve issues (operational efficiency), or improvements in system performance that enable employee productivity. As one channel expert noted, benchmarks, business reviews, and analytics dashboards have become must-haves for MSPs to prove their value. Clients also “expect more proof of value” – they want to know what was prevented, what improved, how security posture changed, and what’s coming next. Ensuring your data is clean and presented in an accessible way is vital – e.g. an MSP might implement a customer portal where the client can log in anytime to see ticket status, security alerts, and project updates in real time. [channele2e.com] [provaltech.com]
Improving customer experience also involves being proactive and consultative. An MSP should bring new ideas to the client: for instance, recommending a workflow automation tool to an accounting firm client because the MSP knows reducing manual data entry could save them money. This kind of proactive solutioneering shows the MSP is thinking about the client’s business, not just waiting for instructions. Industry trends show that clients in mature markets now expect MSPs to help predict and prevent issues and to speak the language of business outcomes. Instead of waiting for clients to ask for a technology, the MSP should be saying “We’ve analyzed your operations and we think adopting XYZ software could improve your customer satisfaction by 10%, let us help you implement it.” [deskday.com]
Personalization and responsiveness remain key to CX. Simple gestures like having a dedicated account manager who really knows the client’s environment, or sending quick status updates during a major incident, go a long way in building trust. Also, timely support (meeting or exceeding SLAs) is part of the experience – even with automation, MSPs must ensure that when a human touch is needed, they are prompt and effective.
Example Action – Customer Experience: Consider an MSP serving a chain of retail stores. Historically, they just kept the POS systems running. In 2026, the MSP shifts approach: they schedule quarterly strategy sessions with the retailer’s management. In one QBR, they present a dashboard showing that over the holiday season, their support kept 99.9% uptime, preventing an estimated 5 hours of downtime (which, for the retailer, translates to an estimated $50k of sales not lost). They also highlight that by upgrading the store’s Wi-Fi and installing a new inventory management app (their suggestion last quarter), the client’s inventory turnover improved noticeably. Going forward, the MSP recommends a customer analytics tool to help the retailer personalize marketing – a bit outside pure IT infrastructure, but a tech solution aligned to growing the retailer’s business. The client, seeing the MSP’s advice consistently improve outcomes, now views the MSP as a strategic partner rather than just an IT supplier, leading to a long-term contract and openness to more services. [provaltech.com]
In essence, the MSPs that win in 2026 will pair excellent technical service with high-touch, value-driven customer engagement. They will measure their success in the client’s terms (productivity, risk reduction, growth support) and continuously communicate that value. This shift from “vendor” to “partner” status not only improves client satisfaction but provides MSPs with opportunities to broaden their services (since satisfied clients trust them with more tasks). As one MSP CEO put it, support is essential “but strategic guidance becomes the real differentiator”. [provaltech.com]
5. Navigating Compliance and Regulatory Demands
In a world of escalating data regulations and industry-specific rules, compliance has become a critical area where MSPs need to step up. SMBs often lack dedicated compliance officers or expertise, so they look to their MSPs for help in governing IT systems according to laws and standards. Current state: Not all MSPs currently include compliance management in their service portfolio. Many focus on technology uptime and security, assuming compliance (e.g., with data privacy laws or industry regulations) is the client’s responsibility. This gap means SMBs might be unaware of vulnerabilities or violations until an audit or breach occurs. Given the proliferation of regulations – from GDPR and CCPA (privacy) to PCI DSS (payment security), HIPAA (health data), or even sector-specific cybersecurity mandates – MSPs that ignore compliance are leaving clients exposed. In 2025, forward-looking MSPs identified compliance as a major opportunity, noting that continuous compliance monitoring and audit support could command premium services. Yet execution is lagging: compliance is often addressed in a piecemeal way (e.g., enabling encryption here or there) rather than through a structured program. [deskday.com]
Focus for 2026: Make compliance and governance a proactive service, not an afterthought. MSPs should familiarize themselves with the key regulations affecting their client base. For example, if you support medical clinics, HIPAA guidelines on data protection and breach notification should be second nature; if you serve European customers, GDPR’s requirements for data handling and breach reporting must be baked into your processes. In practical terms, MSPs need to audit their clients’ systems for compliance gaps regularly. This could entail running tools that check for data that’s stored without proper encryption, or ensuring that access rights are configured according to least privilege principles.
Offering Compliance-as-a-Service (CaaS) can differentiate an MSP. CaaS might include services such as: policy development (helping an SMB craft an IT usage policy or data retention policy), continuous monitoring (monitoring logins, file transfers, and configurations against compliance benchmarks), and automated compliance reporting. For instance, an MSP can use dashboard tools to map a client’s status against frameworks like NIST or ISO 27001, showing which controls are in place and which need attention. Prior to audits or assessments, the MSP can run an “audit readiness” exercise to fix issues. It’s also wise to educate clients – e.g., hold an annual workshop on new laws (such as updates to privacy regulations) that the client needs to know about. [deskday.com]
Compliance efforts go hand-in-hand with security improvements, but have a distinct business value: they reduce risk of legal penalties and build trust with the client’s customers. SMBs may not have realized their MSP could help here, so proactively offering this service in 2026 can meet an unmet need. Industry data suggests MSPs especially in mature markets (US, Canada, EU, ANZ) are starting to adopt a “compliance-first” service design approach, making compliance a core part of every solution due to strict regulations in these regions. This trend will likely spread worldwide as more countries introduce data protection laws. [deskday.com]
Example Action – Compliance: A small finance company (client of an MSP) faces strict regulations (PCI DSS for credit card data and new cybersecurity mandates from their government). The MSP decides in 2026 to create a Compliance Dashboard for this client. Each month, the dashboard scans the client’s systems: checking that all devices have the latest security patches, that antivirus is active, that only approved personnel accessed sensitive databases, and that backups were performed. The MSP shares this dashboard during monthly calls, so the client sees they are, say, 98% compliant with PCI requirements, with specific recommendations to get to 100%. When the client undergoes its annual audit, the MSP helps generate the required reports (e.g. user access logs, incident logs) at a click of a button. The audit passes without major findings – a stark improvement from previous years. The client’s executives now sleep better knowing compliance is continuously watched by their MSP.
In short, MSPs in 2026 should integrate compliance into their offerings to protect clients not just from hackers, but also from regulators. This involves staying current on relevant laws, leveraging tools to automate compliance checks, and guiding clients through the complex maze of requirements. By doing so, MSPs add a layer of strategic value (shielding clients from fines and reputational damage) and strengthen their role as a long-term partner. Given that regulatory scrutiny is only increasing globally, a proactive stance on compliance is both a defensive necessity and a chance to build trust (clients will know their MSP “has their back” on more than just tech). [deskday.com]
6. Driving Efficiency with Process Automation
Operational efficiency is the backbone of MSP profitability and service quality. Yet, many MSPs today are held back by inefficient, manual processes, which translates into slower service for clients and squeezed margins for the MSP. What’s not working: Despite great advancements in management tools, surveys reveal that MSP teams still spend excessive time on low-value, repetitive tasks. For example, one study found MSP staff spend over 100 hours per month on manual chores like re-entering ticket data between systems, preparing reports for QBRs, and reconciling billing—tasks that could be automated. In interviews, managers admitted that engineers spend “half their week” babysitting these processes instead of focusing on higher-level projects. There’s wide acknowledgment (95% of MSP leaders agree) that automation is required for growth, and that repetitive busywork is blocking strategic initiatives. However, most MSPs estimate they’ve automated fewer than 25% of their core workflows so far. The reasons cited include lack of time to set up automations, disparate tools that don’t talk to each other, and the complexity of custom scripting. This is a clear area where MSPs are not doing well enough currently – they know automation is key, but progress has been uneven and slow. [suppfusion.com]
Focus for 2026: The coming year should be when MSPs aggressively streamline and automate their operations. Efficiency isn’t just about saving money – it directly impacts customer satisfaction (faster, error-free service) and the MSP’s ability to scale without adding headcount. Here are key targets for automation:
- Integrating Systems: A major source of inefficiency is when the PSA (professional services automation tool, for tickets/billing) doesn’t integrate with the RMM (remote monitoring and management) or other tools – technicians end up copying data from one system to another. In 2026, MSPs should ensure their core platforms are tightly integrated or consider moving to unified platforms. It’s telling that 95% of MSPs say integrating RMM, PSA, backup, and documentation tools is essential. For instance, if a monitoring alert can automatically generate a ticket in the PSA (with all relevant info attached), and that in turn updates documentation and billing records, it cuts out a lot of swivel-chair work. Many MSPs are pursuing tool consolidation – using fewer, more integrated tools – to achieve this. [kaseya.com] [deskday.com]
- Automating Routine Tasks: Every MSP has a set of mundane tasks that happen daily or weekly – applying patches, updating antivirus definitions, onboarding a new user account, checking backup status, etc. Scripting and RPA (Robotic Process Automation) can handle many of these. By 2026, MSPs should have automated patch management across client devices (with approvals for exceptions), scheduled scripts to resolve common alerts (e.g., auto-restart a service if it stops), and automatic user provisioning workflows (so when a client hires someone, the MSP’s system creates the necessary accounts and permissions through a predefined script). Many MSP tools come with automation capabilities that may be underutilized; now is the time to exploit them fully. As one industry CEO quipped, 2025 was the year of “we should automate that,” and 2026 is the year MSPs must do it – you can’t scale without automation. [provaltech.com]
- Eliminating Duplicate Work in Client Reporting: As discussed in the CX section, account managers often spend hours collating data for client reports. Automating this reporting is a quick win. MSPs can set up their PSA or BI (business intelligence) tools to pull metrics (tickets resolved, SLA compliance, security events) and generate a polished report or dashboard with minimal human input. This might involve adopting a reporting tool or writing some integrations, but it pays off every quarter, and it allows account managers to spend time on analysis rather than assembly. Some MSPs are adopting client-facing dashboards that are always up-to-date, drastically reducing the need to manually build slide decks. [suppfusion.com]
- Workflow Automation and AI Ops: Beyond individual tasks, MSPs should examine end-to-end workflows for automation opportunities. For instance, when a monitoring alert comes in (say CPU usage high on a server), a fully automated workflow might create a ticket, run a diagnostic script on the server, attach the results to the ticket, and if a simple threshold condition is met (like a runaway process), even attempt a remediation (kill or restart the process). If that fixes it, the system closes the ticket with notes; if not, it escalates to a human. Achieving such “self-healing” workflows is increasingly possible with AI Ops tools and advanced scripting. The concept of a “Zero-Touch MSP” – where AI handles 90% of tickets and routine changes – is on the horizon and some SMB-focused MSPs will start approaching that model by mastering their vendors’ automation features. [techaisle.com]
To get there, MSPs should overcome barriers by allocating time for automation projects (maybe dedicating a staff member a few hours a week to building automations) and leveraging community scripts and best practices. The new generation of MSP owners, often backed by private equity, are already pushing for this operational efficiency as a mandate. [suppfusion.com], [suppfusion.com]
Example Action – Automation: A 20-person MSP found its engineers were drowning in repetitive tasks and using 10+ different tools that didn’t sync well. In 2026, they embarked on an “Automation Sprint”: First, they consolidated from 3 separate monitoring and ticketing systems to a single unified platform to reduce context switching. Next, they identified the top 5 daily tasks that ate up engineer time – patching Windows, adding new Office365 accounts for clients, resetting passwords, updating tickets, and compiling monthly reports. They created scripts for each: patches now deploy automatically with reports of success/failure; a simple form was built for clients to request new accounts which triggers an automated user creation in all relevant systems; a self-service password reset tool was rolled out; ticket updates between their systems and a major client’s system were linked via API to stop double entry. They also set up a dashboard that pulls data from their PSA to auto-generate QBR slides. Over a few months, they measured a reduction of ~120 hours of busywork per month across the team. Technicians now spend those hours on project work and learning new skills, which benefits both the MSP and its clients through faster project delivery and more informed staff. [kaseya.com] [suppfusion.com]
The lesson is clear: streamlining operations through automation is no longer optional. In 2026, the most successful MSPs will be those who have turned efficiency into a competitive advantage – enabling them to offer faster response times, more consistent service, and even innovative pricing models (because automation can reduce the cost to serve). Clients ultimately benefit from this through fewer errors and quicker service. As MSP commentary notes, the new wave of MSP leadership “expects operational efficiency and scalability” and will prioritize automation and data-driven processes to stay competitive. MSPs should do the same, treating automation not as a one-off project but as an ongoing discipline (continuously finding new ways to eliminate waste and streamline as tools evolve). [suppfusion.com]
7. Investing in Workforce Development and Talent
Behind every successful MSP is a skilled and motivated team. In 2026, human talent remains irreplaceable – even as AI and automation handle more tasks – because people drive the complex problem-solving, relationship management, and strategic planning that set top MSPs apart. The problem: The MSP industry is facing serious talent challenges. There’s a well-documented shortage of IT professionals, especially in high-demand areas like cybersecurity and cloud architecture. According to industry surveys, 52% of MSPs identify hiring and recruiting as their primary challenge, and 68% of IT leaders in MSPs struggle to find cloud and security expertise. The talent gap often forces MSPs to either overwork their existing staff or turn down business. Indeed, burnout is an issue: nearly 40% of MSP techs were working 50+ hour weeks in recent years and 59% had to work through holidays to keep up with workload. Such strain leads to high turnover, which creates a vicious cycle of understaffing. [deskday.com] [kaseya.com]
Moreover, MSPs sometimes underinvest in training their staff. In the rush of daily operations, keeping engineers’ skillsets up-to-date (with new certifications or learning emerging technologies) can fall by the wayside. This leaves teams ill-prepared for new service offerings (like managing a new cloud platform or a new security tool) that clients might demand.
Focus for 2026: MSPs need a multi-pronged strategy to build and maintain a strong workforce, treating talent as a long-term investment:
- Upskilling and Continuous Learning: Make 2026 the year your MSP implements a formal training program. This could include paying for certifications (e.g. Azure/AWS certifications, cybersecurity certs like CISSP, vendor-specific courses for popular tools). It might mean allocating each engineer a certain number of training hours per quarter that are sacrosanct. By upskilling existing employees, MSPs can fill skill gaps internally. For example, turning a good systems admin into a cloud architect through a structured learning path benefits the MSP far more than trying to hire a cloud architect in a tight market. As one MSP CEO advises, “the MSPs that grow will be the ones that develop the people they already have.”. Also, encourage knowledge sharing within the team (senior engineers mentoring juniors, internal workshops, etc.), which can accelerate learning and increase engagement. [provaltech.com]
- Use External Support to Augment Staff: When hiring is tough, lean on creative solutions like outsourcing or partnerships. Many MSPs are turning to white-label service providers or contractors for certain functions – e.g. using an outsourced Network Operations Center (NOC) or Security Operations Center (SOC) service that operates under the MSP’s brand. This way, you can offer 24/7 coverage or specialized skills (like advanced cybersecurity analysis) without having to hire for every role. Notably, white-label partnerships have grown ~80% over three years in the MSP space. For an MSP, this could mean partnering with a third-party to handle after-hours support or level-1 tickets, relieving your core team at night. Or outsourcing complex tasks like mobile app support to a niche firm. The key is to convert fixed labor costs into flexible resources – scaling up when needed, scaling down when not, while your clients still experience a seamless service. In 2026, MSPs should evaluate which services are better done in-house versus through partners, and not be afraid to offload non-core or hard-to-hire areas. [deskday.com]
- Improve Work-Life Balance and Retention: Recognize that burnout will cause you to lose the talent you have. MSP leadership should institute policies to protect their teams from perpetual overwork. This might involve hiring ahead of demand when possible, using automation (as above) to remove after-hours pager fatigue, and enforcing time-off so people can recharge. Flexible work arrangements (remote work options, which are common now) can help retain employees too. Additionally, create clear career paths within the MSP. One reason people leave is the feeling of stagnation; show your techs how they can progress to senior roles, lead specialist positions, or even vCIO-type consulting roles as they grow. Regular 1:1s discussing career goals and aligning training to those goals can improve morale and loyalty. [provaltech.com]
- Leverage Vendor Training and Communities: Many tech vendors (Microsoft, Cisco, security vendors, etc.) offer extensive training resources for their partners. In the next year, make sure to tap into these vendor-backed training programs. For example, if a new security product is launched that you plan to offer, send engineers to the vendor’s certification course early. Encouraging staff to participate in MSP communities or events (like user groups, webinars, industry conferences) can also spark new ideas and professional growth, which they bring back to your business. The channel is expecting more vendor support in this area – so take advantage of it. [channele2e.com]
Example Action – Workforce: A growing MSP of 15 employees had trouble hiring senior cloud engineers in 2025. In 2026, they took a different approach: they identified two junior techs with interest in cloud and enrolled them in an accelerated Azure training program (funded by the MSP). Within months, those juniors earned certifications and started taking on cloud project work under supervision, filling much of the gap. To cover overnight shifts, the MSP contracted with a reputable NOC service that would handle alerts from midnight to 6 AM, so their on-call engineers could actually rest at night. They also instituted “Tech Fridays” – every second Friday afternoon, the company sets aside client work and all staff focus on learning: taking an online course, lab time, or sharing knowledge with peers. This became a valued perk and led to cross-training (e.g. the security specialist taught a class on advanced firewall management to others). By year-end, employee satisfaction (measured via survey) was up significantly, the MSP’s attrition dropped to near-zero, and their enhanced skills meant they could offer new services (like Azure database management) without external hires.
In summary, solving the talent puzzle is vital for 2026. MSPs should treat their employees as their greatest asset, because they are. A combination of developing internal talent, easing workloads through smart resourcing and automation, and fostering a positive work environment will pay dividends. Not only will this ensure you have the skills to deliver all the advanced services discussed (security, cloud, AI, etc.), but clients will notice stability and expertise in their interactions (frequent turnover or junior, untrained support is a red flag to many customers). Given the tight labor market, MSPs that invest in people will be the ones with the capacity to grow and innovate, whereas those that neglect it may find they can’t meet client needs or quality standards due to staffing shortfalls.
Conclusion: Succeeding in 2026 – From MSP to Business Partner
Entering 2026, MSPs globally – especially those catering to SMBs – must retool and refocus across these critical operational areas. The overarching theme is moving up the value chain: from putting out IT fires to delivering strategic prevention; from offering generic services to providing specialized, client-tailored solutions; from using people for every task to harnessing automation and AI for scalability. The challenges are real – cyber threats are more serious, technology is more complex, competition is fiercer, and clients are more demanding. But so are the opportunities: SMBs are investing heavily in technology and rely on MSPs more than ever for expertise. The MSPs that proactively improve in the areas discussed – security, cloud, AI, customer success, compliance, efficiency, and talent – will position themselves to capture this growth. [deskday.com]
It’s worth noting that in mature IT markets, clients now expect MSPs to behave almost like consulting partners with automation engines, blending advisory insight with flawless execution. This is a useful vision for 2026: an MSP that can talk business outcomes, ensure compliance and security, implement cutting-edge tech (cloud/AI) smoothly, and continually optimize its own operations behind the scenes. Achieving all of this at once is daunting, so MSPs should prioritize incrementally: for example, “secure first, automate second” – shoring up cybersecurity and compliance before layering fancy AI, since automation without security just accelerates risk. They should also pick a focus – mastering one vertical or technical specialty at a time – rather than try to do everything broadly. [deskday.com]
By addressing what is not being done well today and committing to these improvements, MSPs can transform their businesses in 2026. The payoff will be stronger customer relationships (and contract renewals), higher margins (through efficiency and premium services), and sustainable growth even in competitive markets. In contrast, MSPs that cling to the old break-fix, “one-size-fits-all” mindset will increasingly struggle – facing commoditization and client churn as they fail to meet rising standards. [deskday.com]
In conclusion, 2026 is set to be a pivotal year for the MSP industry. It will reward providers who are bold and strategic – those who invest in AI and automation, build deep security and compliance capabilities, tailor their services to client needs, and nurture talented teams. MSPs that embrace these changes will not just survive the evolving landscape, they will thrive as indispensable partners in their customers’ success. The blueprint is clear; now it’s about execution. As the industry saying goes, the MSPs who evolve will lead, and those who don’t will be left behind. By focusing on the areas outlined above, MSPs can ensure they are on the leading side of that equation in 2026.